MajesTEC‑1 Primary Safety Analysis
Among patients who received TECVAYLI®, 47% were exposed for 6 months or longer and 7% were exposed for one year or longer.
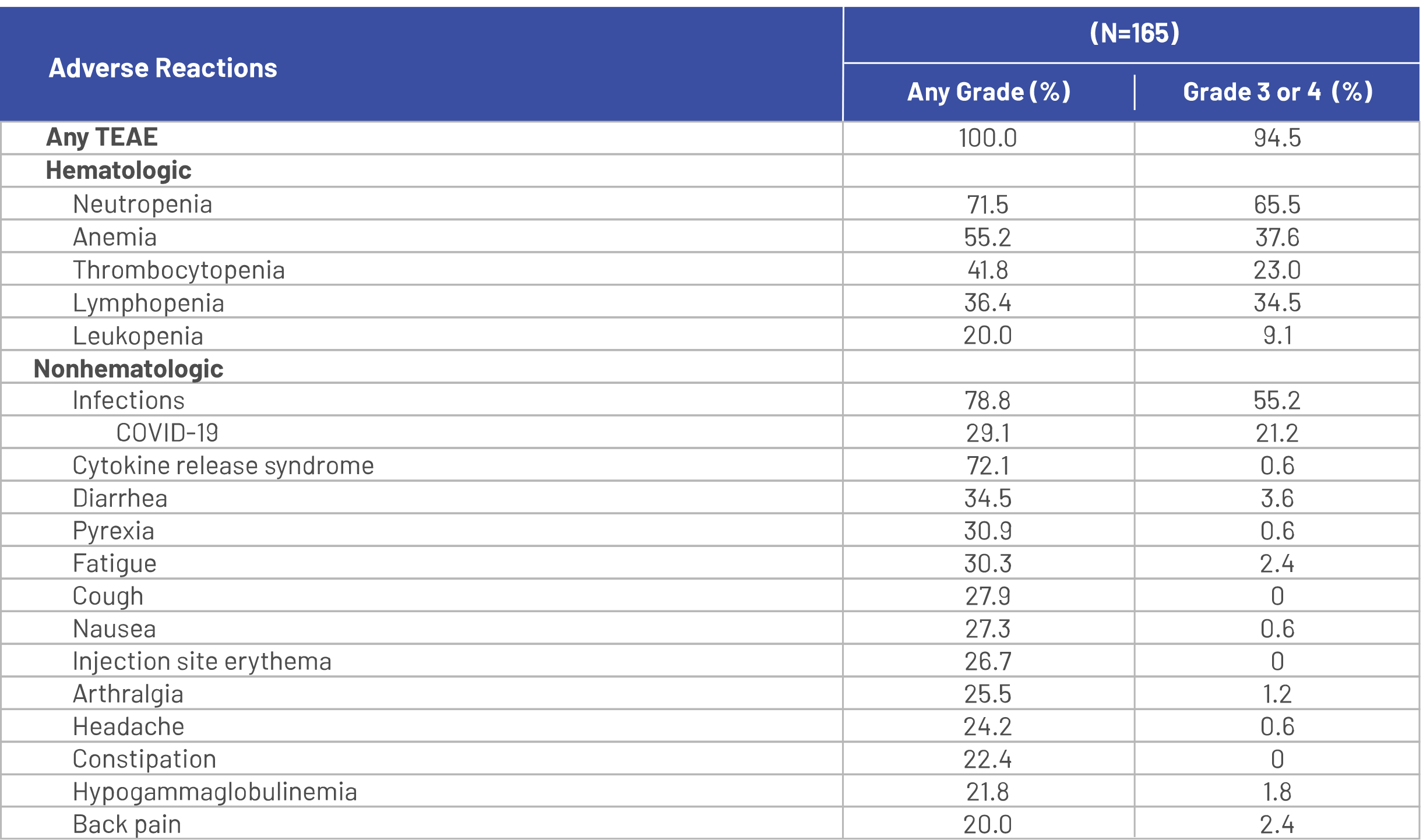
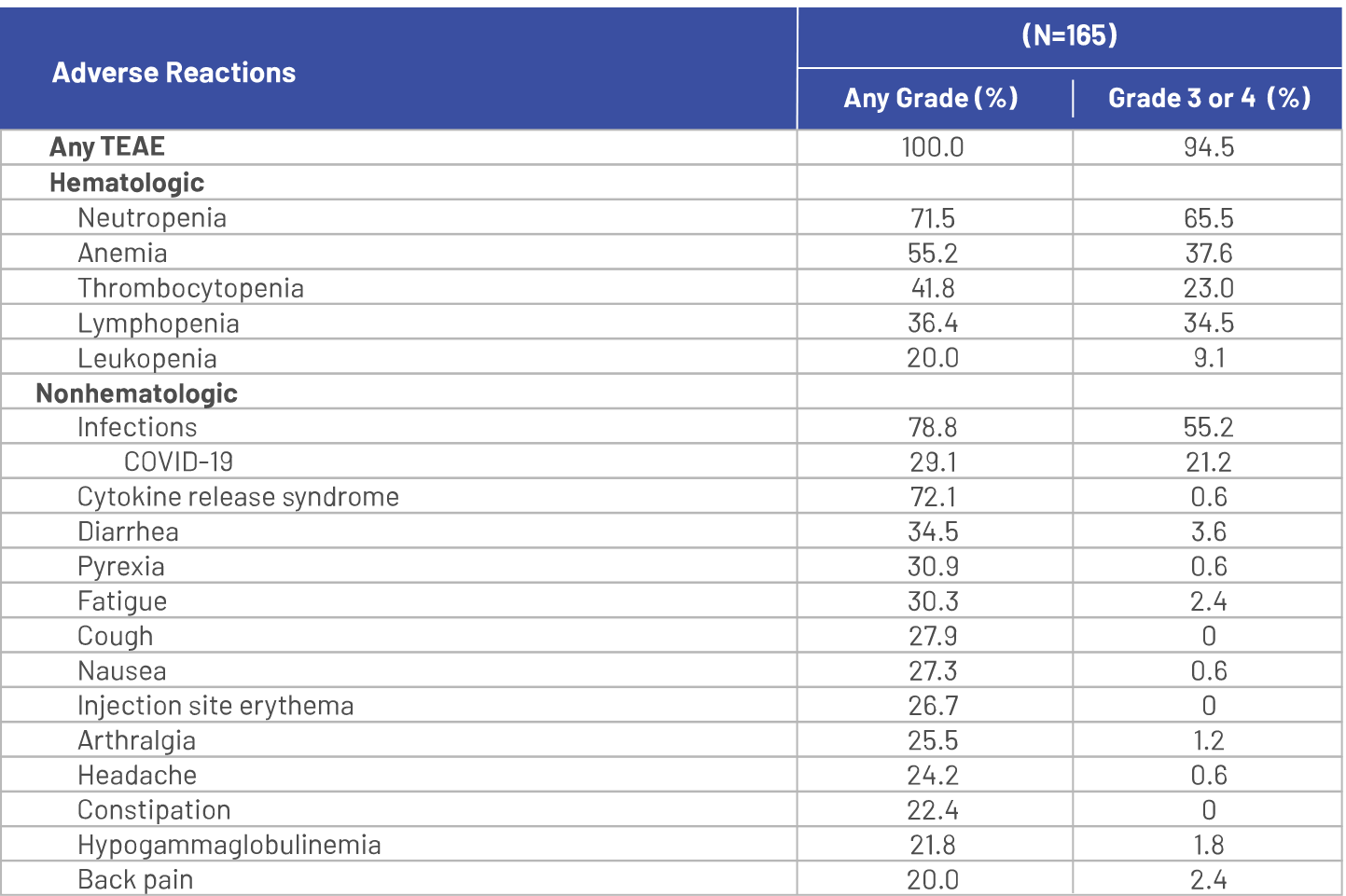
Serious adverse reactions occurred in 54% of patients who received TECVAYLI®. Serious adverse reactions in >2% of patients included pneumonia (15%), cytokine release syndrome (8%), sepsis (6%), general physical health deterioration (6%), COVID‑19 (6%), acute kidney injury (4.8%), pyrexia (4.8%), musculoskeletal pain (2.4%), and encephalopathy (2.4%).1
Fatal adverse reactions occurred in 5% of patients who received TECVAYLI®, including COVID‑19 (1.8%), pneumonia (1.8%), septic shock (0.6%), acute renal failure (0.6%), and hemoperitoneum (0.6%).1
Permanent discontinuation of TECVAYLI® due to adverse reactions occurred in 1.2% of patients. Adverse reactions resulting in permanent discontinuation of TECVAYLI® included pneumonia (adenoviral and pneumocystis jirovecii pneumonia in the same patient) and hypercalcemia.1
Dosage interruptions of TECVAYLI® due to an adverse reaction occurred in 73% of patients. Adverse reactions which required dosage interruption in >5% of patients included neutropenia, pneumonia, pyrexia, cytokine release syndrome, upper respiratory tract infection, and COVID‑19.1
Clinically relevant adverse reactions in <10% of patients who received TECVAYLI® included febrile neutropenia, sepsis, ICANS, seizure, Guillain‑Barré syndrome, hepatic failure, and new onset or reactivated viral infections [including adenovirus, hepatitis B virus (HBV), cytomegalovirus (CMV), varicella zoster virus (VZV), herpes simplex virus (HSV) and progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy (PML)].1
Please see Table 11 in the full Prescribing Information for a summary of laboratory abnormalities in MajesTEC‑1.1
Adverse reactions (≥10%) in patients with RRMM treated with TECVAYLI® in the MajesTEC-1 trial primary analysis1
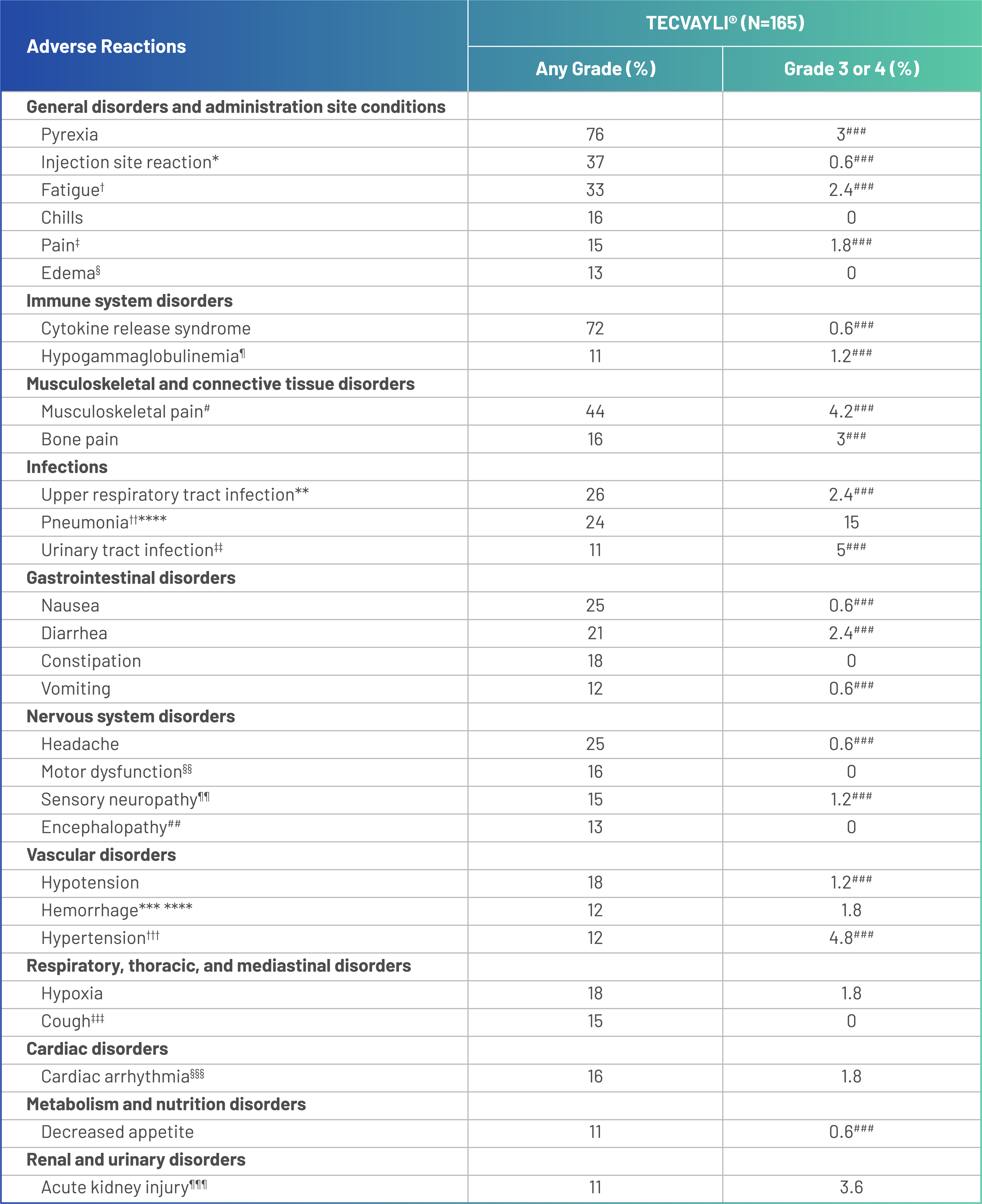
ASTCT, American Society for Transplantation and Cellular Therapy; COVID-19, coronavirus disease 2019; CRS, cytokine release syndrome; CTCAE, Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events; RRMM, relapsed or refractory multiple myeloma.
Adverse reactions were graded based on CTCAE Version 4.03, with the exception of CRS, which was graded per ASTCT 2019 criteria.
*Injection site reaction includes application site erythema, injection site bruising, injection site cellulitis, injection site discomfort, injection site erythema, injection site hematoma, injection site induration, injection site inflammation, injection site edema, injection site pruritus, injection site rash, injection site reaction and injection site swelling.
†Fatigue includes asthenia and fatigue.
‡Pain includes ear pain, flank pain, groin pain, oropharyngeal pain, pain, pain in jaw, toothache and tumor pain.
§Edema includes face edema, fluid overload, fluid retention, edema peripheral and peripheral swelling.
¶Hypogammaglobulinemia includes hypogammaglobulinemia and hypoglobulinemia.
#Musculoskeletal pain includes arthralgia, back pain, muscle discomfort, musculoskeletal chest pain, musculoskeletal pain, myalgia, neck pain, non-cardiac chest pain and pain in extremity.
**Upper respiratory tract infection includes bronchitis, influenza like illness, nasopharyngitis, pharyngitis, respiratory tract infection, respiratory tract infection bacterial, rhinitis, rhinovirus infection, sinusitis, tracheitis, upper respiratory tract infection and viral upper respiratory tract infection.
††Pneumonia includes COVID-19 pneumonia, enterobacter pneumonia, lower respiratory tract infection, metapneumovirus pneumonia, pneumocystis jirovecii pneumonia, pneumonia, pneumonia adenoviral, pneumonia klebsiella, pneumonia moraxella, pneumonia pneumococcal, pneumonia pseudomonal, pneumonia respiratory syncytial viral, pneumonia staphylococcal and pneumonia viral.
‡‡Urinary tract infection includes cystitis, cystitis escherichia, cystitis klebsiella, escherichia urinary tract infection, urinary tract infection and urinary tract infection bacterial.
§§Motor dysfunction includes cogwheel rigidity, dysgraphia, dysphonia, gait disturbance, hypokinesia, muscle rigidity, muscle spasms, muscular weakness, peroneal nerve palsy, psychomotor hyperactivity, tremor and VIth nerve paralysis.
¶¶Sensory neuropathy includes dysesthesia, hypoesthesia, hypoesthesia oral, neuralgia, paresthesia, paresthesia oral, peripheral sensory neuropathy, sciatica and vestibular neuronitis.
##Encephalopathy includes agitation, apathy, aphasia, confusional state, delirium, depressed level of consciousness, disorientation, dyscalculia, hallucination, lethargy, memory impairment, mental status changes and somnolence.
***Hemorrhage includes conjunctival hemorrhage, epistaxis, hematoma, hematuria, hemoperitoneum, hemorrhoidal hemorrhage, lower gastrointestinal hemorrhage, melena, mouth hemorrhage and subdural hematoma.
†††Hypertension includes essential hypertension and hypertension.
‡‡‡Cough includes allergic cough, cough, productive cough and upper-airway cough syndrome.
§§§Cardiac arrhythmia includes atrial flutter, cardiac arrest, sinus bradycardia, sinus tachycardia, supraventricular tachycardia, tachycardia and ventricular tachycardia.
¶¶¶Acute kidney injury includes acute kidney injury and renal impairment.
###Only Grade 3 adverse reactions occurred.
****Includes the following fatal adverse reactions: hemorrhage (n=1), pneumonia (n=3).
Dose reductions are not recommended with TECVAYLI®1
Dose interruptions of TECVAYLI® due to adverse reactions occurred in 73% of patients, and the most frequent (>5%) leading to dose interruptions were:
- Neutropenia
- Pneumonia
- Pyrexia
- CRS
- Upper respiratory tract infection
- COVID-19
Dosage delays may be required to manage toxicities related to TECVAYLI®.
1.2% of patients receiving TECVAYLI® permanently discontinued treatment due to adverse reactions in the primary analysis1
- The adverse reactions resulting in permanent discontinuation of TECVAYLI® included pneumonia (adenoviral and pneumocystis jirovecii pneumonia in the same patient) and hypercalcemia
Discontinuation rates due to adverse reactions in MajesTEC‑112

Adverse reactions resulting in permanent discontinuation of TECVAYLI® were pneumonia (adenoviral and pneumocystis jirovecii pneumonia in the same patient) and hypercalcemia.

Adverse reactions resulting in permanent discontinuation of TECVAYLI® were COVID-19 in 2 patients; progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy, sepsis, arthralgia, arthritis, and brain neoplasm in 1 patient each; and events of pneumocystis jirovecii pneumonia and pneumonia adenoviral in the same patient, and hypercalcemia.
*This informations is not included in the current full Prescribing Information.
Most CRS events were Grade 1 and 2, median time to onset was 2 days, and median duration was 2 days1
*CRS, including life threatening or fatal reactions, may occur in patients receiving TECVAYLI®.
†In the primary analysis, CRS of any grade was reported in 72% of patients.

Median time to onset: 2 days (range: 1-6 days) after most recent dose
Median duration: 2 days (range: 1-9 days)
Most CRS events occurred during the step-up dosing period, and incidence decreased with subsequent doses1
Recurrent CRS occurred in 33% of patients in the primary analysis.


Signs and symptoms of CRS may include:
- Fever
- Hypoxia
- Chills
- Hypotension
- Sinus tachycardia
- Headache
- Elevated liver enzymes (aspartate aminotransferase and alanine aminotransferase elevation)
If not already hospitalized, at the first sign of CRS, immediately evaluate patient for hospitalization. Administer supportive care based on severity and consider further management per current practice guidelines. Withhold or permanently discontinue TECVAYLI® based on severity.
TECVAYLI® is available only through a restricted program under a REMS.
Patient counseling
Advise the patient to read the FDA-approved patient labeling (Medication Guide).
Discuss the signs and symptoms associated with CRS, including fever, hypoxia, chills, hypotension, sinus tachycardia, headache, and elevated liver enzymes. Advise patients to immediately contact their healthcare provider if they experience signs or symptoms of CRS.
- Fever (100.4°F or higher)
- Feeling anxious
- Difficulty breathing
- Confusion or restlessness
- Chills
- Headache
- Dizziness or lightheadedness
- Increased liver enzymes in their blood
- Fast heartbeat
Advise patients that they will be hospitalized for 48 hours after administration of all doses within the TECVAYLI® step-up dosing schedule.